SHREK NEWS
Basic composition and failure analysis of laparoscopic system
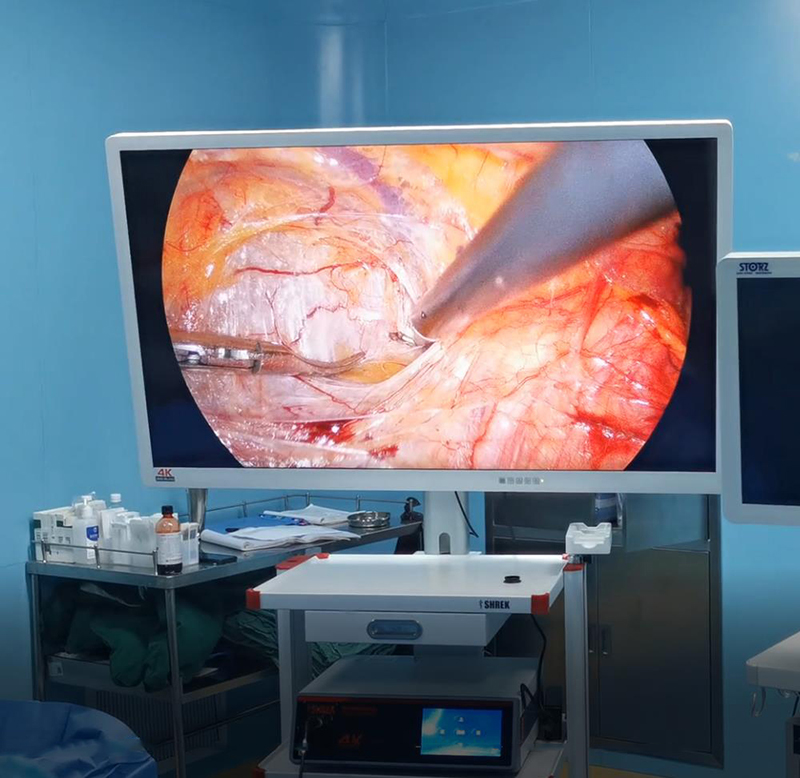
A laparoscopic system is a medical device used in minimally invasive surgery. It consists of several components, including a video camera, a light source, a monitor, a laparoscope, and surgical instruments.
The laparoscope is a long, thin tube that is inserted into the body through a small incision. It contains a camera that captures high-quality images of the surgical site, which are transmitted to a monitor. The light source provides illumination, allowing the surgeon to see the area more clearly. The surgical instruments, such as graspers, scissors, and dissectors, are inserted through additional incisions and are used to manipulate and cut tissue.
Failure of a laparoscopic system can occur due to a variety of reasons, including mechanical failure, damage to the camera or instruments, and user error. Mechanical failure can occur if the device is not maintained properly or if it is subjected to excessive force during use. Damage to the camera or instruments can occur if they come into contact with sharp or hard objects, such as bones or metal tools. User error can also lead to failure, such as incorrect use of the instruments or incorrect positioning of the laparoscope.
To analyze the failure of a laparoscopic system, the device may need to be disassembled and inspected. This can help to identify any mechanical or structural issues that may have led to the failure. The camera and instruments can also be inspected to determine if they have been damaged or worn out. Additionally, a review of the surgical procedure may be necessary to identify any user errors or issues with the system's setup or operation.
Overall, the composition and failure analysis of a laparoscopic system involve a thorough understanding of its components and their functions, as well as an understanding of the surgical procedures for which it is used. Proper maintenance and careful use of the device can help to minimize the risk of failure and ensure the best possible outcomes for patients.




