SHREK NEWS
What is the function of endoscopic equipment?
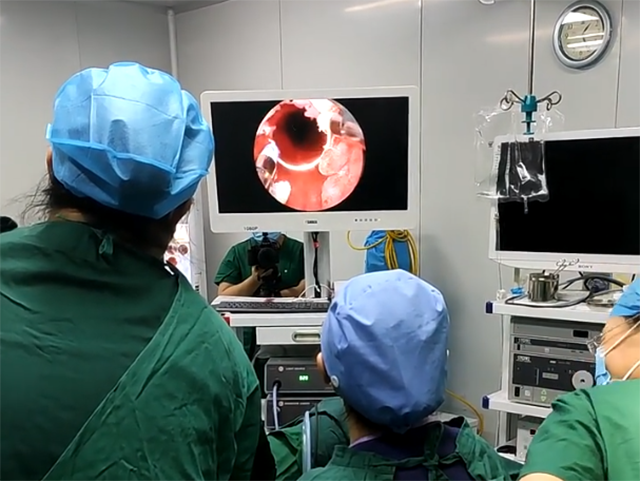
The function of endoscopic equipment is to enable medical professionals to perform minimally invasive procedures to visualize and diagnose internal organs and structures of the body. Endoscopic equipment typically consists of a flexible or rigid endoscope, a camera system, a light source, and a monitor.
The endoscope is a thin, flexible or rigid tube that is inserted into the body through a natural opening or a small incision. The endoscope has a camera and light source at its tip, which captures high-quality images of the area being examined. The camera system transmits these images to a monitor, where the medical professional can view them in real-time.
The light source illuminates the area being examined, and the camera captures the images of the internal organs and structures. The monitor displays the images captured by the camera system, providing a clear and detailed view of the area being examined.
The endoscopic equipment allows medical professionals to visualize and diagnose a wide range of medical conditions. Endoscopic procedures can be used to examine the digestive system, the respiratory system, the urinary system, the reproductive system, the joints, and other internal structures.
Endoscopic equipment can also be used to perform minimally invasive procedures, such as removing polyps or tumors, taking biopsies, or repairing damaged tissue. These procedures are less invasive than traditional surgery, resulting in reduced pain, faster recovery times, and fewer complications for the patient.
Overall, the function of endoscopic equipment is to provide medical professionals with a minimally invasive way to visualize and diagnose internal organs and structures, enabling them to provide faster, more accurate diagnoses and treatments for a wide range of medical conditions.




