SHREK NEWS
Indications and contraindications of nasal endoscope
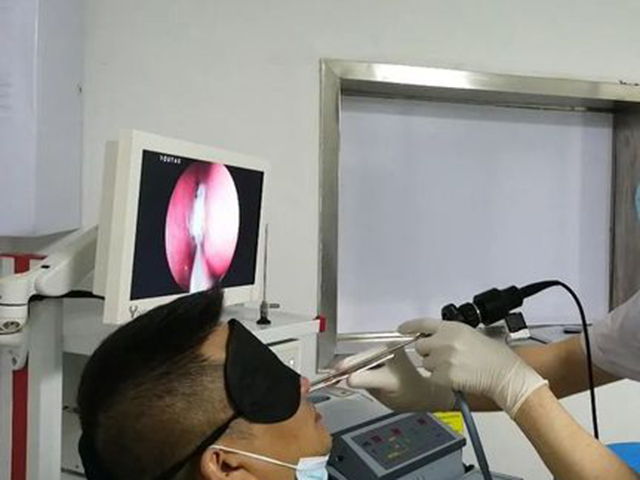
Nasal endoscopy is a medical procedure that involves the use of a flexible or rigid endoscope to visualize the nasal cavity and its surrounding structures. It can be used for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes in various medical specialties, including otolaryngology (ear, nose, and throat), pulmonology, and neurology.
Indications for Nasal Endoscopy:
Chronic sinusitis: Nasal endoscopy can help identify the cause of chronic sinusitis, such as nasal polyps or a deviated septum.
Nasal obstruction: Nasal endoscopy can help identify the cause of nasal obstruction, such as a nasal tumor or septal deviation.
Epistaxis (nosebleeds): Nasal endoscopy can help identify the source of the bleeding, such as a blood vessel abnormality or tumor.
Allergies: Nasal endoscopy can help identify allergic rhinitis, which is inflammation of the nasal passages due to an allergic reaction.
Foreign body: Nasal endoscopy can help identify the presence of a foreign object in the nasal cavity.
Sleep apnea: Nasal endoscopy can help identify obstructions in the upper airway that may be contributing to sleep apnea.
Contraindications for Nasal Endoscopy:
Recent nasal surgery: Nasal endoscopy should be avoided in patients who have recently undergone nasal surgery, as it may cause bleeding or damage to the surgical site.
Severe nasal congestion: Nasal endoscopy may not be possible in patients with severe nasal congestion, as the endoscope may not be able to pass through the nasal cavity.
Nasal trauma: Nasal endoscopy should be avoided in patients who have recently suffered nasal trauma, as it may cause further injury.
Bleeding disorders: Nasal endoscopy should be avoided in patients with bleeding disorders, as it may cause excessive bleeding.
Uncooperative patients: Nasal endoscopy requires cooperation from the patient, as it can cause discomfort or a gag reflex. It may be contraindicated in patients who are unable to tolerate the procedure.




