SHREK NEWS
veterinary video endoscope manufacturer: the process of use of vet endoscopy and observation methods
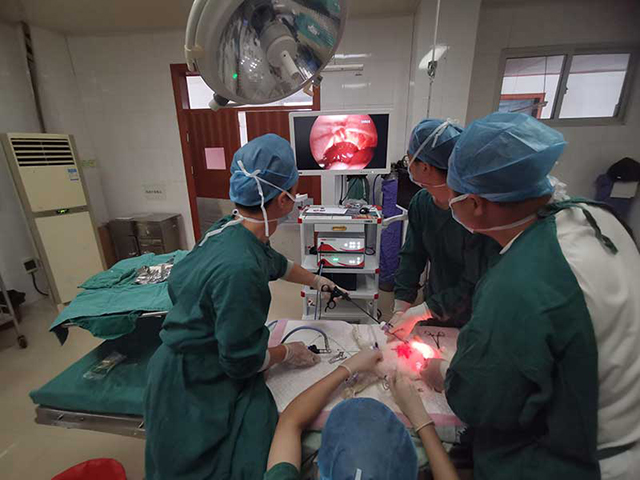
veterinary video endoscope is a medical device used to visualize the internal organs and structures of animals. It is a long, thin, flexible tube that has a camera and light source at the tip, which allows veterinarians and other animal health professionals to see inside the animal's body without making large incisions.
The process of using an animal endoscope typically involves the following steps:
Preparation: The animal is typically sedated or anesthetized to ensure that it remains still during the procedure. The area where the endoscope will be inserted (such as the mouth or anus) is cleaned and sterilized to reduce the risk of infection.
Insertion: The endoscope is inserted into the animal's body through the appropriate orifice (such as the mouth or anus) and carefully guided towards the area of interest. As the endoscope moves deeper into the animal's body, the camera at the tip of the device sends images back to a monitor, allowing the veterinarian to see the internal structures in real-time.
Observation: Once the endoscope is in place, the veterinarian can begin to observe the internal structures of the animal. This may involve taking still images or videos for later analysis, or it may involve real-time observation of the animal's organs and tissues.
Removal: Once the observation is complete, the endoscope is carefully removed from the animal's body.
Observation methods using veterinary video endoscope can vary depending on the specific type of animal and the area of the body being examined. However, some common observation methods include:
Gastrointestinal endoscopy: This involves inserting an endoscope into the animal's mouth or anus and observing the inside of the digestive system. This can be used to diagnose conditions such as stomach ulcers, gastrointestinal blockages, and inflammatory bowel disease.
Bronchoscopy: This involves inserting an endoscope into the animal's airways and lungs to observe the respiratory system. This can be used to diagnose conditions such as asthma, bronchitis, and lung tumors.
Laparoscopy: This involves inserting an endoscope through a small incision in the animal's abdomen to observe the internal organs. This can be used to diagnose conditions such as liver disease, kidney disease, and tumors.
Arthroscopy: This involves inserting an endoscope into a joint to observe the interior of the joint. This can be used to diagnose conditions such as arthritis, torn ligaments, and joint infections.
Overall, veterinary video endoscope are important tools for diagnosing and treating a variety of conditions in animals. By providing a non-invasive way to visualize internal structures, they can help veterinarians make accurate diagnoses and provide targeted treatment.




