SHREK NEWS
Application of ear endoscope in otorhinolaryngology
Ear endoscopes are a specialized type of medical instrument used in otorhinolaryngology (ENT) to examine the ear canal and middle ear. These endoscopes are designed to provide a detailed, magnified view of the ear structures, which can help healthcare providers diagnose and treat a variety of ear-related conditions.
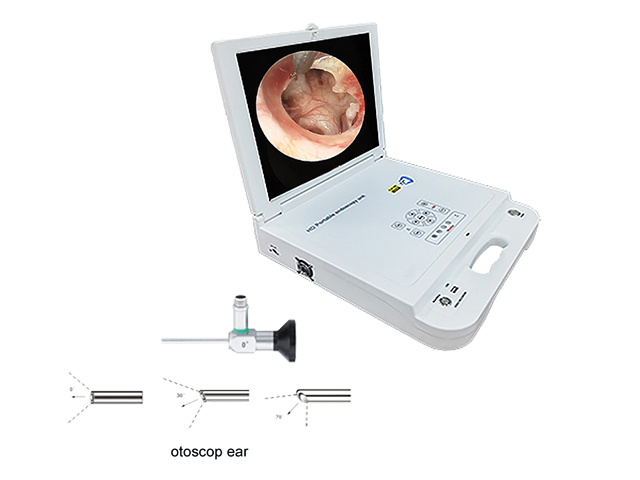
Some of the specific applications of ear endoscopy in ENT include:
Diagnosis of ear infections: Ear endoscopy can help healthcare providers identify signs of infection in the ear canal and middle ear, such as inflammation, fluid accumulation, or pus.
Assessment of ear wax buildup: Excessive ear wax can cause hearing loss and discomfort, and ear endoscopy can help providers evaluate the extent of the buildup and determine the best course of treatment.
Evaluation of ear trauma: Ear endoscopy can be used to examine the ear structures for signs of injury or trauma, such as a ruptured eardrum or foreign object in the ear canal.
Examination of ear tumors or growths: Ear endoscopy can help healthcare providers visualize and biopsy any abnormal growths or tumors in the ear canal or middle ear.
Evaluation of hearing loss: Ear endoscopy can help identify structural abnormalities or other factors that may be contributing to hearing loss.
Guidance for ear surgery: Ear endoscopy can provide a detailed view of the ear structures to guide surgical procedures, such as the removal of tumors or repair of a ruptured eardrum.
Overall, ear endoscopy is a valuable tool in the diagnosis and treatment of a wide range of ear-related conditions, and it allows for a minimally invasive approach to evaluation and treatment. Patients experiencing any ear-related symptoms should discuss the potential benefits of ear endoscopy with their healthcare provider.




